What is a hybrid inverter
What is a hybrid inverter?
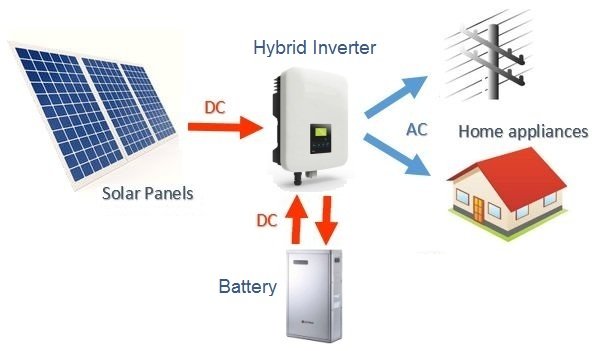
A hybrid inverter is an all-in-one inverter that incorporates both a solar and battery inverter in one simple unit. This enables storage of excess solar energy in a battery system for self-use. Hybrid inverters function like a common grid-tie solar inverter but can generally operate in one of several different modes, depending on the application. This includes battery backup mode, which provides a limited level of backup power in the event of a blackout. Most hybrid inverters can operate without a battery and function like a grid-tie solar inverter by exporting excess solar energy to the electricity grid.
Having all the key features for solar and battery storage in one simple plug-and-play inverter means hybrid inverters are generally much lower cost and easier to install compared to more complex off-grid inverter systems. However, they have several limitations and are generally not recommended for permanent off-grid installations.
Do hybrid inverters cost more than regular solar inverters?
Hybrid inverters generally cost 30 to 40% more compared to the equivalent size solar inverters due to the increased complexity and additional components. However, they are cheaper and easier to install compared to dedicated off-grid inverters. For example, an average 5kW solar inverter costs around $1100, a 5kW hybrid inverter costs closer to $1500, and a standard 5kW off-grid inverter costs $2500. Additionally, for hybrid systems to provide backup power, most household switchboards need to be modified or upgraded, which adds to the total cost of installation.
3 to 5kW hybrid inverter price range = $1000 to $2500
6 to 10kW hybrid inverter price range = $2000 to $5500
7 to 10kW hybrid/off-grid inverters price = $2500 to $7500
How do hybrid inverters work?
Hybrid inverters are advanced inverters that can operate in different modes depending on household power consumption and backup power requirements. Much like regular solar (string) inverters, hybrid inverters convert solar DC power from strings of solar panels to AC (alternating current) power used to power your home. Any excess solar energy is then used to charge a connected battery system. To manage the power flow, hybrid inverters require an external energy meter (often called a CT meter) to measure the household power use and determine when excess power is available to charge the battery. The meter also provides load data so the inverter can discharge the battery to power the household loads when required.
Most hybrid inverters can be programmed to function in four different modes:
Goodwe ES hybrid inverter with 2 x 5kWh batteries
Grid-tie mode - Functions like a normal solar inverter (no battery)
Hybrid mode - Stores excess solar energy during the day to be used in the evening to increase self-sufficiency.
Backup mode - Functions like a normal solar inverter when the grid is connected and automatically switches to backup power mode during a grid outage
Off-grid mode* - Operates much like an off-grid inverter and uses excess solar to charge the battery and power the loads without a grid connection.
Only a select few hybrid inverters are designed for off-grid solar systems and have the features to start and run a backup power source, such as a generator if required. Hybrid inverters with off-grid mode include Ingeteam and Deye (Sol-Ark). Hybrid inverters are affordable for average households who want to be more self-sufficient using solar and batteries but don't intend to disconnect from the grid or experience frequent blackouts. Refer to our complete hybrid and batter comparison charts for a direct comparison of hybrid inverters and battery storage systems.
Three main types of hybrid inverters
Basic hybrid inverter for solar storage
Hybrid inverter for solar storage and backup power
Battery energy storage systems (BESS)
Some hybrid inverters do not have backup power capability as standard and require additional (optional) backup boxes and equipment in order to provide backup power in the event of a blackout. BESS systems are essentially a hybrid inverter with an inbuilt lithium battery in one complete package, usually about the size of a fridge. However, like most appliances, there are many features and capabilities that differentiate the wide variety of BESS systems available. See our detailed BESS comparison chart for more information.
Backup Power Supply
Sungrow hybrid inverter with battery and add-on backup power box.
To function as a backup power supply, a hybrid inverter must be able to isolate from the grid during a blackout and use battery power to back up any household essential circuits**. Most modern hybrid inverters have the ‘grid isolation’ feature built-in, but some hybrid inverters do not; this means they cannot operate in either backup or off-grid mode. However, often, an additional backup box or EPS (emergency power supply) is available to enable this feature. If grid stability is not an issue, then this simple type of hybrid inverter would be a good economical choice.
More advanced hybrid inverters can operate in backup mode indefinitely and even function completely off-grid, providing the loads are manageable, and there is adequate sunlight all year round. However, dedicated off-grid inverters and high-capacity batteries are recommended for off-grid solar systems due to the high continuous and surge power rating required to run a whole house completely off-grid.
**Essential circuits are basic load circuits that can be easily backed up during a blackout. This includes simple things like lights, fridges, TV's and computers. To back up an entire house generally requires a more powerful AC or DC-coupled multi-mode inverter or an off-grid system.
Off-grid Vs Hybrid Inverters
Most modern off-grid inverters, sometimes called multi-mode, are much more advanced and powerful inverters that can operate with or without a grid AC connection and offer instantaneous backup in the event of a blackout. These inverters can also back up large loads like air-conditioners, pumps and heaters. Many advanced multi-mode off-grid inverters also have very high pass-through power capability, so separation of essential and non-essential loads is not required.
Read more about the best off-grid inverters and systems here.
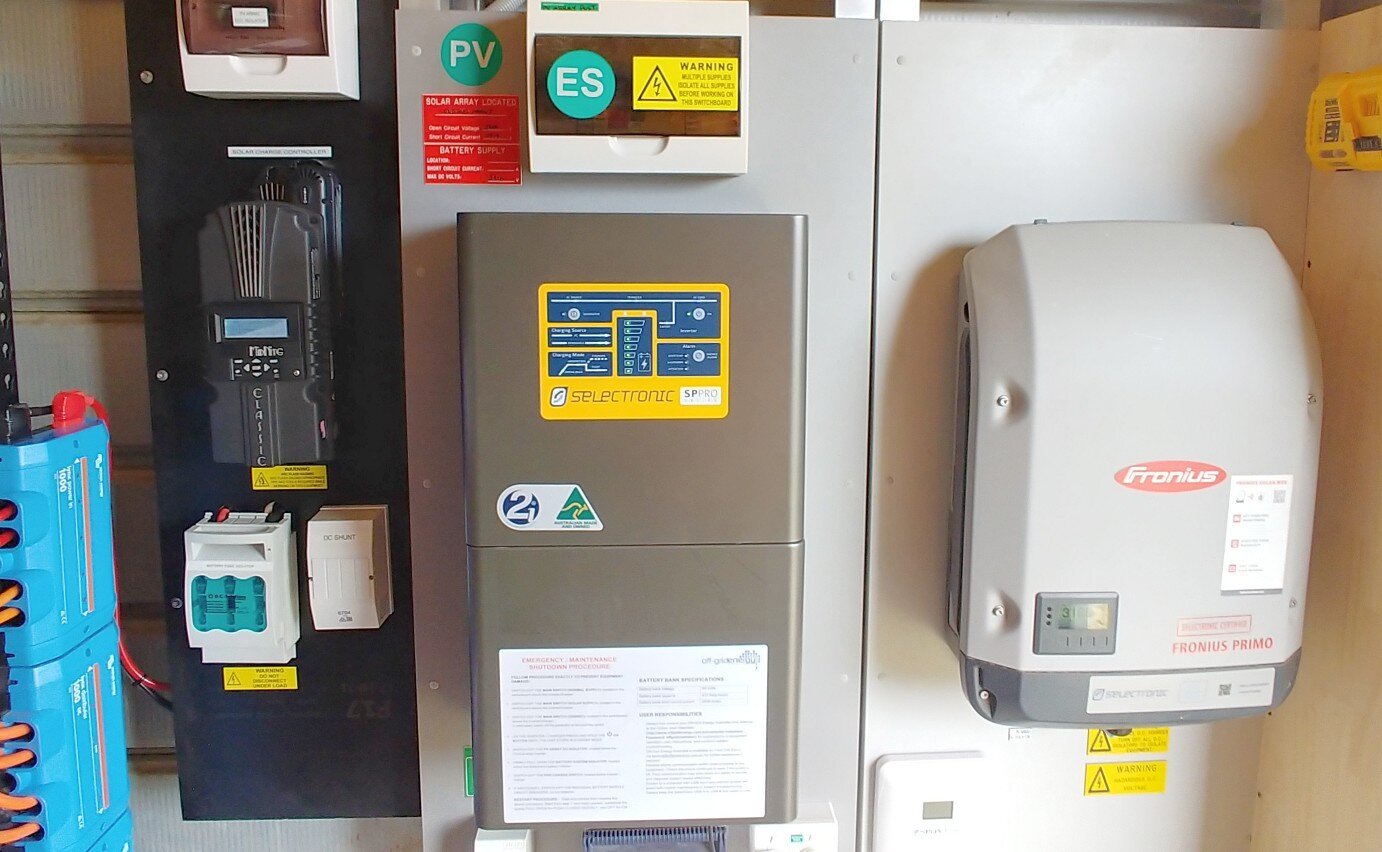
A powerful Selectronic multi-mode hybrid & off-grid inverter AC coupled with a Fronius solar inverter.






We review the best home smart EV chargers for maximising rooftop solar-generated electricity and reducing grid consumption. Plus, we explain how dynamic load-balancing works, examine the latest smart EV charging features and the various apps used to configure and monitor each charger.